For many households across the United Kingdom, heating oil isn’t a choice — it’s a necessity.
If you live in a rural village, countryside cottage, or anywhere beyond the mains gas network, heating oil is likely what keeps your radiators warm and your showers hot.
Yet surprisingly, many homeowners rely on oil every day without truly understanding how it works, how to manage it efficiently, or how to save money long term.
This guide is designed to change that.
Drawing on years of industry knowledge and real-world homeowner experience, here’s a clear, practical, and uniquely UK-focused explanation of heating oil — from storage and consumption to pricing habits, system care, and future changes.
Let’s start at the beginning.
What Exactly Is Heating Oil in the UK?
Heating oil is a liquid fuel stored on your property and burned inside an oil boiler to provide:
-
Central heating
-
Hot water
-
Sometimes cooking (in older systems)
In UK homes, the fuel used is almost always kerosene (28-second oil). It’s refined specifically for domestic boilers and burns cleaner than heavier oils.
Unlike gas or electricity, heating oil is delivered in bulk by tanker and stored in your own tank. You become your own “mini energy supplier” — responsible for monitoring levels and ordering refills.
That single difference changes everything about how you manage your heating.
How an Oil Heating System Works (Step by Step)
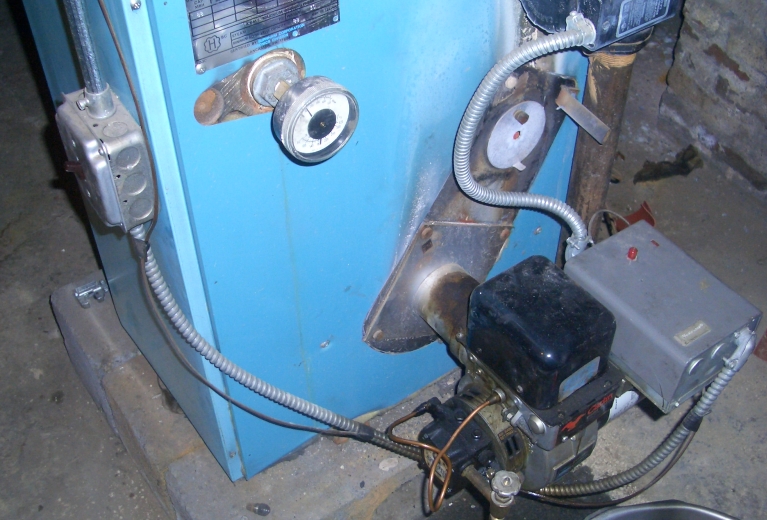



Your oil heating system follows a simple but powerful process:
1. Oil Storage
Fuel sits in your external tank — usually in the garden or beside the house.
2. Demand for Heat
When your thermostat drops below the set temperature, it signals the boiler.
3. Fuel Delivery
Oil travels through a pipe from the tank to the boiler burner.
4. Combustion
The burner atomises the oil into a fine mist and ignites it.
5. Heat Transfer
The flame heats water inside the boiler, which then circulates through radiators or underfloor pipes.
6. Hot Water
The same heated water supplies your taps and showers via a cylinder or combi system.
Everything happens automatically — until the tank runs dry.
Why Heating Oil Still Makes Sense for Many UK Homes
Despite growing talk of renewables, oil remains common — especially outside towns and cities.
Here’s why:
Powerful Heating Performance
Oil produces intense heat, making it ideal for large or older properties that struggle to warm up.
Independence from the Grid
No gas pipes. No standing charges. You control when and where you buy fuel.
Flexible Buying
You can shop around, buy in bulk, or time purchases when prices dip.
Modern Efficiency
Today’s condensing oil boilers can exceed 90% efficiency when properly maintained.
Works with Hybrid Systems
Oil boilers can now integrate with solar panels or heat pumps for reduced carbon impact.
Typical Heating Oil Usage in UK Homes
Every household differs, but realistic annual averages look like this:
| Property Type | Approximate Annual Use |
|---|---|
| Small bungalow | 1,000–1,400 litres |
| Average family home | 1,500–2,500 litres |
| Large rural property | 2,500–4,000+ litres |
Your actual usage depends on:
-
Insulation quality
-
Window type
-
Ceiling height
-
Occupancy
-
Boiler age
-
Lifestyle habits
Homes with solid walls and poor loft insulation often burn 30–40% more oil than modern insulated properties.
Understanding Oil Tanks: More Important Than Most People Realise
Your tank is the heart of your entire heating system.
Single Skin Tanks
One layer of plastic or steel. Cheaper, but offer no protection if the tank leaks.
Bunded Tanks
Double-layered with built-in spill containment. Now recommended (and often required) for environmental safety.
Tank Lifespan
Most tanks last 15–25 years depending on exposure, base quality, and maintenance.
Things Every Homeowner Should Check
-
Is the tank level?
-
Any cracks or bulging?
-
Is vegetation touching it?
-
Does the gauge move freely?
-
Is the base solid?
A neglected tank is the most common cause of costly oil leaks.
When Should You Buy Heating Oil?
Unlike gas, heating oil prices fluctuate daily.
Experienced UK homeowners usually follow these principles:
Buy Outside Peak Season
Late spring and summer often bring lower prices due to reduced demand.
Don’t Wait Until Empty
Emergency winter orders are almost always more expensive.
Refill at ¼ Tank
This gives flexibility to wait for better prices while avoiding run-out.
Consider Group Buying
Local communities sometimes combine orders for better rates.
Planning beats panic — every time.
The Real Cost of Heating Oil (Beyond the Price Per Litre)
Many people only look at fuel price. Smart homeowners look at total system cost.
Consider:
-
Boiler servicing (£100–£150 annually)
-
Tank maintenance or replacement
-
Filter changes
-
Efficiency losses in older boilers
-
Heat escaping through poor insulation
Improving insulation often saves more money than chasing the cheapest oil delivery.
Is Heating Oil Being Phased Out in the UK?
New build homes can no longer install oil boilers.
However:
-
Existing homes may continue using oil
-
Replacement boilers are still permitted
-
There’s no deadline forcing current users to switch
The future is gradual transition — not sudden removal.
Many households are preparing by:
-
Improving insulation first
-
Adding solar panels
-
Exploring hybrid heating systems
-
Installing smart controls
Oil isn’t vanishing overnight — but efficiency matters more than ever.
Practical Ways to Cut Heating Oil Consumption (That Actually Work)
These aren’t gimmicks — they’re proven:
-
Insulate loft to at least 270mm
-
Install radiator reflector panels
-
Use weather stripping on doors
-
Lower thermostat by just 1°C
-
Heat only occupied rooms
-
Service boiler annually
-
Replace old pumps and controls
Even modest changes can reduce oil use by 15–25%.
Frequently Asked Questions – Heating Oil in the UK
How often should I check my oil level?
Weekly in winter. Monthly in summer.
What happens if I run out completely?
Your boiler will shut down. After refilling, air must be bled from the system — sometimes requiring professional help.
Can heating oil go off?
Yes. After about 12–18 months, oil can degrade and form sludge.
Is heating oil dangerous?
It’s non-explosive and safer than petrol, but leaks can damage soil and foundations if ignored.
How long does an oil boiler last?
Typically 15–20 years with regular servicing.
Can I move away from oil gradually?
Yes. Many homeowners add solar or hybrid systems first, then transition fully later.
Final Thoughts
Heating oil remains a vital energy source for a huge portion of UK homes — especially beyond city limits. While it requires more hands-on management than gas, it offers independence, strong heating performance, and flexibility when used wisely.
Understanding your system, caring for your tank, improving insulation, and buying strategically can dramatically reduce costs while keeping your home comfortable year-round.
Heating oil works best when you stay in control — not when you leave it until the tank runs dry.